Meniscus Tear & Meniscus Repair
Some Meniscal Tears can be repaired by suturing (stitching) the torn pieces together. Whether a tear can be successfully treated with repair depends upon the type of tear, as well as the overall condition of the injured Meniscus. Because the Meniscus must heal back together, recovery time for a repair is much longer than Meniscectomy.
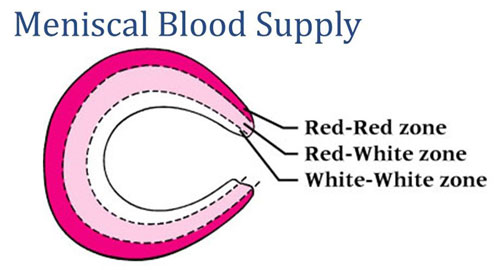
Vascularity of Meniscus
- The Meniscus is divided into three zones. The white-white zone (more than 5 mm from periphery) is the central zone, which has no blood supply at all. Tears in this zone cannot be repaired.
- The Red-White zone (within 3 mm to 5 mm from periphery) is the mid zone of the Meniscus which has minimal blood supply. Tears in this zone may be repaired depending on the type of tear and duration since injury.
- Red-Red Zone (within 3 mm of periphery) is the peripheral zone which is at the Meniscocapsular Junction and is rich in blood supply. Tears in this zone may be repaired with good results.
Indications for Repair:
Any peripheral non-degenerative and longitudinal tears < 3cm in size are indicated for repair.
Relative Contraindications:
Tears greater than 3 cm do not seem to heal after repair. Flap Tears, Radial Tears, Cleavage Tears, or Vertical Tears with secondary lesions that extend into a vascular inner 2/3 of Meniscus heal poorly after repair. Ligamentous instability is a relative contraindication to repair.
Types of Repair:
Outside-to-Inside Arthroscopic Technique:
Main advantage is that there is a low risk of Neurovascular Injury, since needles are precisely passed through the capsule;
Main disadvantage is that suture placement through the Meniscus may not be precise.
Inside-to-Outside Arthroscopic Technique:
The advantage of this technique is it allows for precise placement of sutures in the Meniscus.
The disadvantage of this technique is it does not allow for precise placement of sutures through the capsule, and therefore there is some potential for Neurovascular Injury.
The equipments required for this repair are:
- Single or double barrel cannula system;
- Table spoon or small spade retractor;
- Longkeith needles w/either 2-0 or O absorbable or nonabsorbable.
All-Inside Meniscal Repair:
This is the latest technique for repair of the Meniscus with the help of disposable devices in which the Meniscus is repaired by suture anchors. The advantage of this technique is no knots are to be tied under the skin and no additional incisions are required. The disadvantage of this treatment is the cost increases by many folds.
Disposable Devices

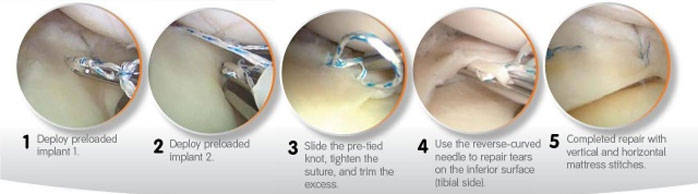
Important points your Arthroscopic Knee Surgeon may consider during repair:
- Enough sutures are placed to avoid gaps of more than 3-5 mm.
- Suture placement is an important aspect of repair.
- The sutures can be placed in horizontal, oblique or vertical direction.
- The Vertical Suture placement may be stronger due to the circumferential orientation of the collagen bundles.
- Horizontal Sutures are almost as strong as vertical sutures, but are more apt to cause eversion of the opposite Meniscal Surface.
- If there is an associated ACL Tear the Meniscus Repair is done first followed by ACL Tear Reconstruction at the same sitting.
Rehabilitation:
The three early post-operative rehabilitation goals are; get the Knee out fully straight, decrease swelling and regain quadriceps muscle control. Patients are encouraged to do straight leg raises in the brace immediately after surgery. The brace is used to walk with the Knee in extension for six weeks. Range of motion is generally started soon after surgery from 0-90 degrees, without any weight-bearing during motion. The brace is unlocked at six weeks and weaned off when good quadriceps control is demonstrated. Motion is increased as tolerated at six weeks, but deep squats are avoided until 12 weeks. Low impact type activities such as swimming and exercise machines are encouraged at 12 weeks, with advancement to cutting and pivoting sports generally at 16 weeks. The assistance of a physical therapist is very helpful in achieving a rapid full recovery.
In the hands of an experienced Arthroscopic Surgeon in Mumbai, Arthroscopic Meniscus Repair is effective outpatient surgical procedure to repair torn Knee Meniscus. The Torn Meniscus is repaired by a variety of minimally invasive techniques and requires post-operative protection to allow healing. Physical therapy is useful to regain full function of the Knee, which occurs on average 4-5 months after surgery.
